EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS — Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System EC-11
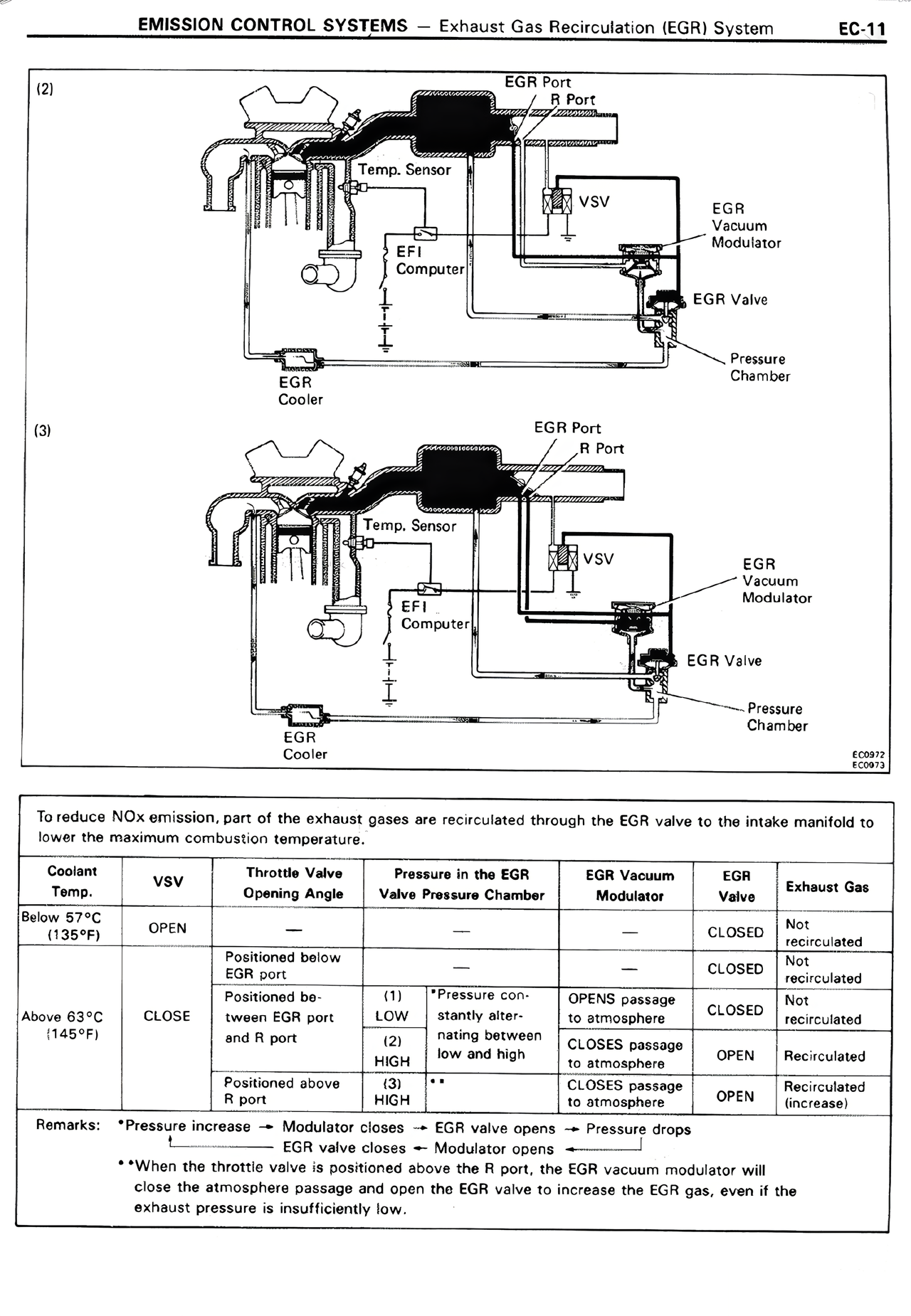
(2)
[Diagram showing EGR system with EGR Port, R Port, Temp. Sensor, VSV, EFI Computer, EGR Vacuum Modulator, EGR Valve, Pressure Chamber, EGR Cooler]
(3)
[Diagram showing similar EGR system with EGR Port, R Port, Temp. Sensor, VSV, EFI Computer, EGR Vacuum Modulator, EGR Valve, Pressure Chamber, EGR Cooler]
E02912
E02913
To reduce NOx emission, part of the exhaust gases are recirculated through the EGR valve to the intake manifold to lower the maximum combustion temperature.
Coolant Temp. | VSV | Throttle Valve Opening Angle | Pressure in the EGR Valve Pressure Chamber | EGR Vacuum Modulator | EGR Valve | Exhaust Gas
Below 57°C (135°F) | OPEN | — | — | — | CLOSED | Not recirculated
| | Positioned below EGR port | — | — | CLOSED | Not recirculated
Above 63°C (145°F) | CLOSE | Positioned be- tween EGR port and R port* | (1) LOW (2) HIGH (3) HIGH | *Pressure con- stantly alter- nating between low and high ** | OPENS passage to atmosphere CLOSES passage to atmosphere CLOSES passage to atmosphere | CLOSED OPEN OPEN | Not recirculated Recirculated Recirculated (increase)
| | Positioned above R port | | | |
Remarks: *Pressure increase → Modulator closes → EGR valve opens → Pressure drops
EGR valve closes → Modulator opens →
**When the throttle valve is positioned above the R port, the EGR vacuum modulator will close the atmosphere passage and open the EGR valve to increase the EGR gas, even if the exhaust pressure is insufficiently low.