TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM — Troubleshooting
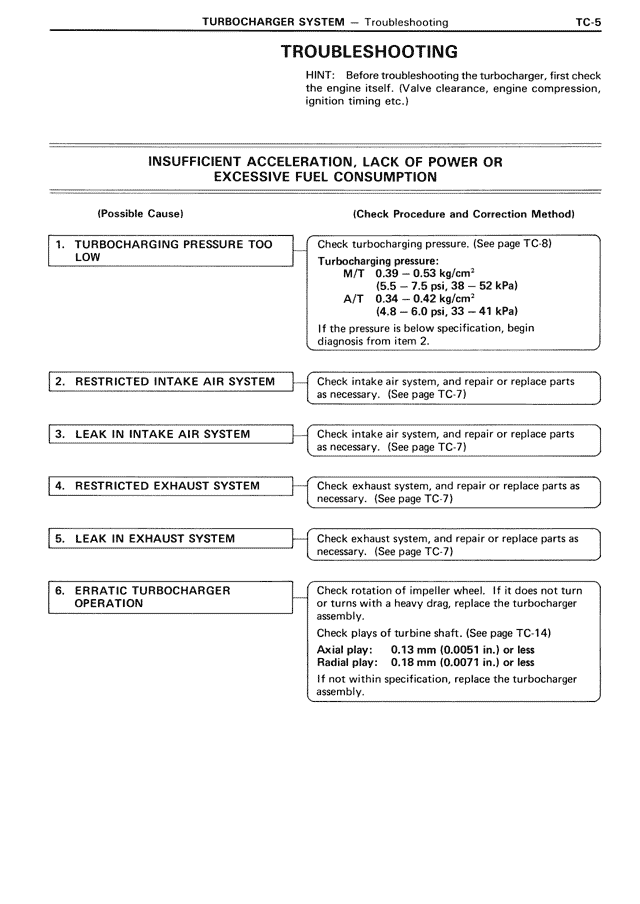
TROUBLESHOOTING
HINT: Before troubleshooting the turbocharger, first check the engine itself. (Valve clearance, engine compression, ignition timing etc.)
INSUFFICIENT ACCELERATION, LACK OF POWER OR EXCESSIVE FUEL CONSUMPTION
(Possible Cause)
1. TURBOCHARGING PRESSURE TOO LOW
2. RESTRICTED INTAKE AIR SYSTEM
3. LEAK IN INTAKE AIR SYSTEM
4. RESTRICTED EXHAUST SYSTEM
5. LEAK IN EXHAUST SYSTEM
6. ERRATIC TURBOCHARGER OPERATION
(Check Procedure and Correction Method)
Check turbocharging pressure. (See page TC-8)
Turbocharging pressure:
M/T 0.39 — 0.53 kg/cm²
(5.5 — 7.5 psi, 38 — 52 kPa)
A/T 0.34 — 0.42 kg/cm²
(4.8 — 6.0 psi, 33 — 41 kPa)
If the pressure is below specification, begin diagnosis from item 2.
Check intake air system, and repair or replace parts as necessary. (See page TC-7)
Check intake air system, and repair or replace parts as necessary. (See page TC-7)
Check exhaust system, and repair or replace parts as necessary. (See page TC-7)
Check exhaust system, and repair or replace parts as necessary. (See page TC-7)
Check rotation of impeller wheel. If it does not turn or turns with a heavy drag, replace the turbocharger assembly.
Check plays of turbine shaft. (See page TC-14)
Axial play: 0.13 mm (0.0051 in.) or less
Radial play: 0.18 mm (0.0071 in.) or less
If not within specification, replace the turbocharger assembly.