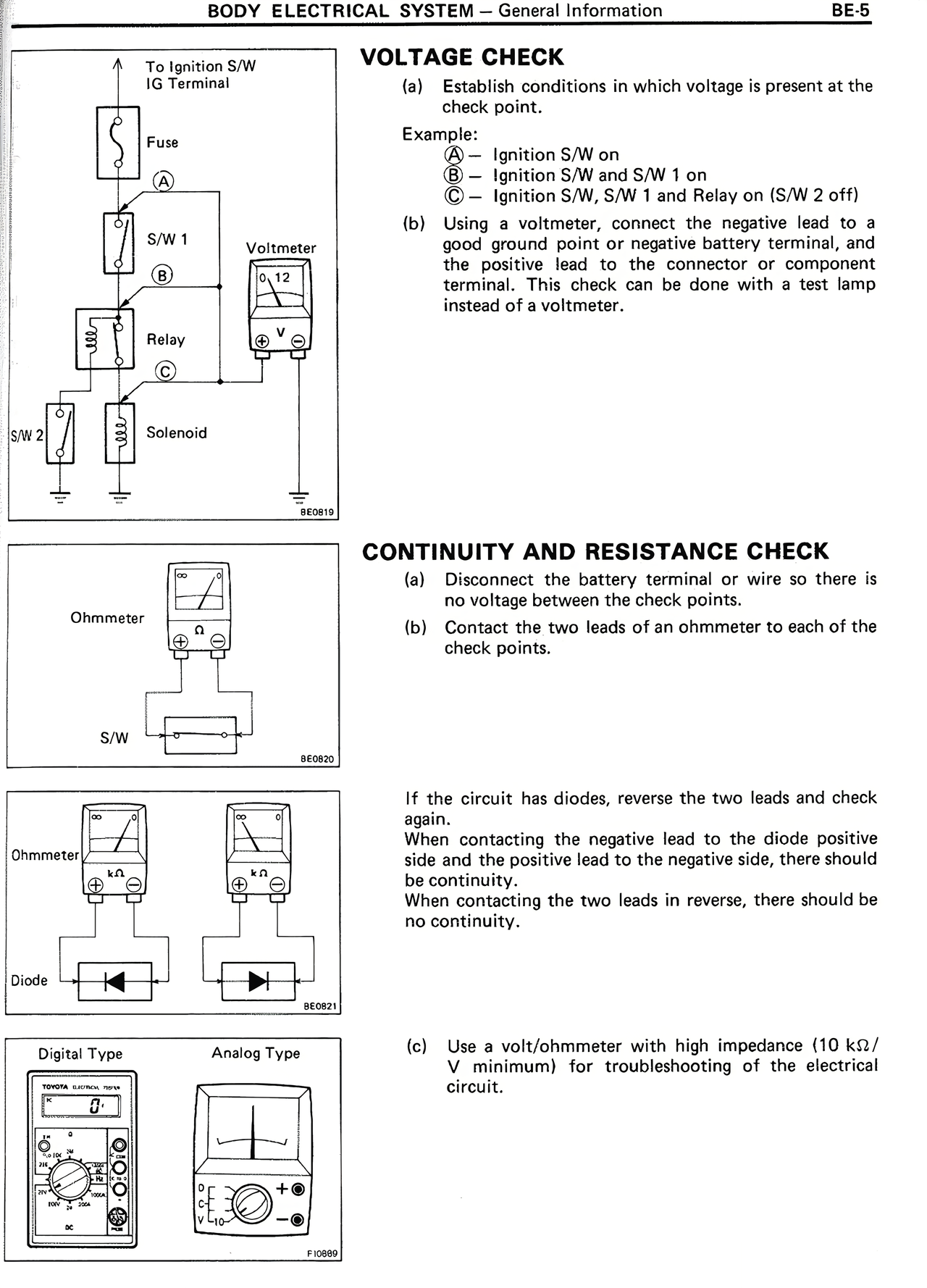
VOLTAGE CHECK
(a) Establish conditions in which voltage is present at the check point.
Example:
A — Ignition S/W on
B — Ignition S/W and S/W 1 on
C — Ignition S/W, S/W 1 and Relay on (S/W 2 off)
(b) Using a voltmeter, connect the negative lead to a good ground point or negative battery terminal, and the positive lead to the connector or component terminal. This check can be done with a test lamp instead of a voltmeter.
CONTINUITY AND RESISTANCE CHECK
(a) Disconnect the battery terminal or wire so there is no voltage between the check points.
(b) Contact the two leads of an ohmmeter to each of the check points.
If the circuit has diodes, reverse the two leads and check again.
When contacting the negative lead to the diode positive side and the positive lead to the negative side, there should be continuity.
When contacting the two leads in reverse, there should be no continuity.
(c) Use a volt/ohmmeter with high impedance (10 kΩ/V minimum) for troubleshooting of the electrical circuit.