IN–21
INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
[1] CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSIS
In troubleshooting, the problem symptoms must be confirmed accurately and all preconceptions must be cleared away in order to give an accurate judgment. To ascertain just what the problem symptoms are, it is extremely important to ask the customer about the problem and the conditions at the time it occurred.
Important Points in the Problem Analysis
The following 5 items are important points in the problem analysis. Past problems which are thought to be unrelated and the repair history, etc. may also help in some cases, so as much information as possible should be gathered and its relationship with the problem symptoms should be correctly ascertained for reference in troubleshooting. A customer problem analysis table is provided in the troubleshooting section for each system for your use.
Important Points in the Customer Problem Analysis
• What ..................... Vehicle model, system name
• When ..................... Date, time, occurrence frequency
• Where ..................... Road conditions
• Under what conditions?.............. Running conditions, driving conditions, weather conditions
• How did it happen? ..................... Problem symptoms
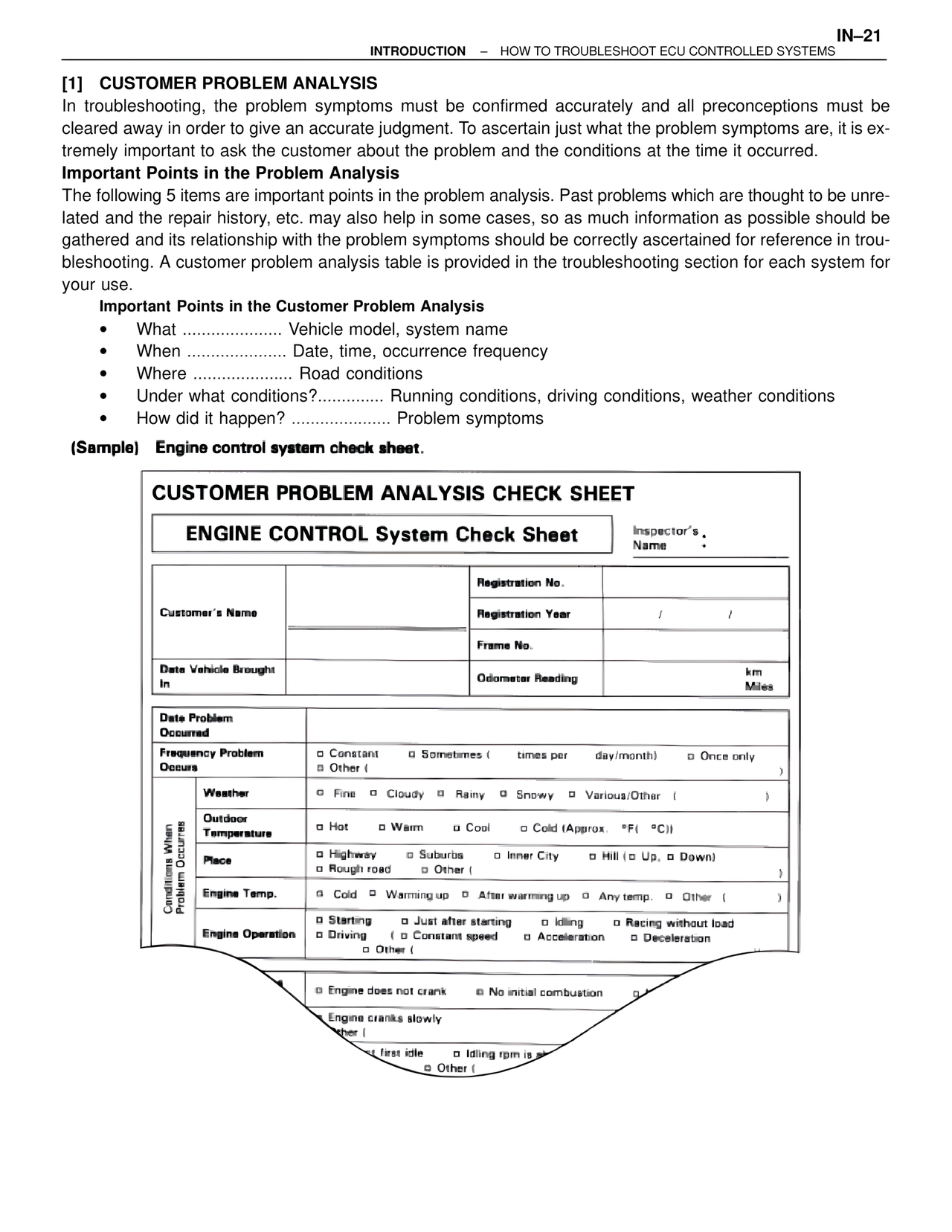
(Sample) Engine control system check sheet.
CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSIS CHECK SHEET
ENGINE CONTROL System Check Sheet
Inspector's Name
Customer's Name
Registration No.
Registration Year / /
Frame No.
Date Vehicle Brought In
Odometer Reading km
Miles
Date Problem Occurred
Frequency Problem Occurs
□ Constant □ Sometimes ( times per day/month) □ Once only
□ Other (
)
Conditions When Problem Occurs
Weather
□ Fine □ Cloudy □ Rainy □ Snowy □ Various/Other (
)
Outdoor Temperature
□ Hot □ Warm □ Cool □ Cold (Approx. °F( °C))
Place
□ Highway □ Suburbs □ Inner City □ Hill (□ Up, □ Down)
□ Rough road □ Other (
)
Engine Temp.
□ Cold □ Warming up □ After warming up □ Any temp. □ Other (
)
Engine Operation
□ Starting □ Just after starting □ Idling □ Racing without load
□ Driving ( □ Constant speed □ Acceleration □ Deceleration
□ Other (
□ Engine does not crank □ No initial combustion □
Engine cranks slowly
□ ther (
□ t first idle □ Idling rpm is st
□ Other (